
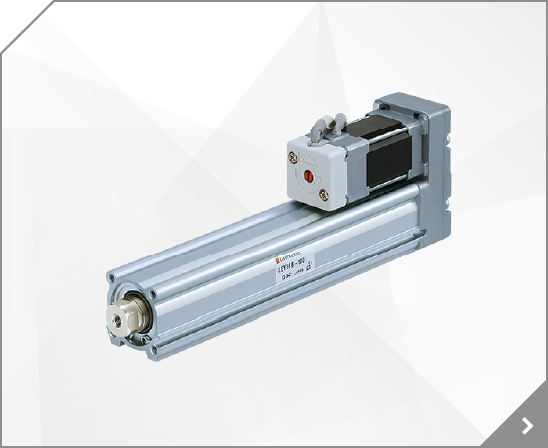
(mm) 4 4 6 6 8 10 Piston rod thread M4 x 0.7 M4 x 0.7 M6 x 1 M6 x 1 M8 x 1.25 M10 x 1.25 Space-saving Port size M 5 x 0.8 M 5 x 0.8 M 5 x 0.8 M 5 x 0.8 G 1/8 G 1/8 Mounting accuracy and rigidity made possible by means of faucet joint and direct mounting.
: Table (2) 1 = W/Wa Find the allowable load weight Wa (kg).
Load rate Ea= K E max Ea=1 0.11=0.11 Work mounting coeficient K: Fig.3 Max. allowable kinetic energy Emax: Table 1 Kinetic energy (E)Allowable kinetic energy (Ea) Possible to use by E=0.0 3 3-1 Load rate of work Calculate static work Wa (N) Wa=1 X 1 X 4=4 K=1 b=1 Wmax=4 a1=1/4=0.25 Wa=K b Wmax Work mounting coeficient K: Fig.3 Allowable load coeficient b: Graph 1 Max.
Allowable moment Wmax: Table 2 1=W/Wa Calculate static moment Wa(N) Wa=1 x 1 x 40=40 K=1 =1 Wmax=40 1=10/40=0.25 Calculate load rate 1 of static moment. 3-2 Load rate of static moment Rolling Yawing Calculate static moment M(Nm).
Section XX 17.8 63 11 18.5 10 7 Bottom view Section XX L 4-NN through Section XX WA Z IA IC 4-MM depth ML 4-OA through 4-OB counter bore depth OL HA: T-slot for hexagon bolt DA DB m IB ID VB VA H X U R T PW 2-Rc P (plug) Rc 1/8 unlocking port Unlocks when pressurized XAH7 depth XL 2-Rc P GC GA PB GB Q S G J K PA + Stroke IE FA FB C + Stroke E B + Stroke XAH7 depth XL A + Stroke (mm) MLGPM
Max.allowable load W max. : Table 2 1=W/Wa 3-2 Load rate of static moment M=W(Ln+An)/1000 Corrected value for center position distance of moment An : Table 3 Ma=M max. Allowable moment coefficient : Graph 2 Max.allowable moment M max. : Table 4 Calculate static moment M(Nm). Examine for Mr [As Mp and My does not arise, Examination is not needed.]
. (3) Allowable load weight coefficient : Graph (1) Wa = 1 x 1 x 4 = 4 K = 1 = 1 Wmax = 4 1 = 0.5/4 = 0.125 Find the allowable load weight Wa (kg).
4 5 WA WB 2 2.5 XA XB 4 5 YC 7 7.5 +0.030 0 +0.030 0 +0.074 0 +0.074 0 +0.030 0 +0.030 0 52H9 65H9 4H9 5H9 7
My = 1 x 9.8 (10 + 30)/1000 = 0.39 A3 = 30 Find the static moment M (Nm). M = W x 9.8 (Ln + An)/1000 Corrected value of moment center position distance An: Table 3 Find the allowable static moment Ma (Nm).
m L Mounting orientation m m Max. speed [mm/s] SpeedVertical Work Load Graph 200 or less Over 200 Graph (Sliding bearing type) q, w t, y u, i Graph (Ball bushing bearing type) e, r o, !
Particle diameter (m) Particle diameter (m) Front matter 23 Comparison of Cleanliness Standards ISO 14644-1 ISO Cass 1 to 9 Intermediate classes available U descriptor: Particles smaller than 0.1 m M descriptor: Particles larger than 5.0 m Standard Fed.Std.209E British unit: Class 1 to 100.000 SI unit: Class M1 to M7 U descriptor: Particles diameter smaller than 0.1 m (SI unit) (British
nt nt is us u t u w C 0 us o 90 k o c lo o C l dj C C 19 dj se c Cl 1 A k A A wi e w oc ge dj k A is oc k ng dj u wi e Cl an st us se ro ra m r ta t ot m r d at ti n e n io on e n e on nt e nt tio nd r r a a ti n n g ta e 5 9 g ta e 9 ro 5 ro m m u im u im ax M ax M Note) The drawing shows the rotation range of the positioning pin hole.
HUMIDITY SWITCH, HUMIDITY SENSOR, Q62, 142.00000 lb
HUMIDITY SWITCH, HUMIDITY SENSOR, Q62, 142.00000 lb
HUMIDITY SWITCH, HUMIDITY SENSOR, Q62, 142.00000 lb
HUMIDITY SWITCH, HUMIDITY SENSOR, Q62, 157.80000 lb
HUMIDITY SENSOR. CONDENSATION CHECKER. 168.50000 lb. Q62.
HUMIDITY SENSOR. CONDENSATION CHECKER. 143.00000 lb. Q62.
IC circuit 5 V 3-wire (NPN) 3-wire (PNP) 2-wire Lead wire length symbols: 0.5 m Nil (Ex.)
Nil (Example) C73C 5 m Z (Example) C73CZ 3 m L (Example) C73CL None N (Example) C73CN C76 C85 Solid state switches marked with are manufactured upon receipt of order.










 C85
C85