
Load mass kg Load mass kg Load mass kg 4 4 4 4 CY1F CY1F 3 3 3 3 CYP CY1F15 CY1F10 CY1F10 CY1F10 2 2 2 2 CY1F10 1 1 1 1 D0.5 500 300 100 50 0.5 500 300 100 50 0.5 500 300 100 50 0.5 500 300 100 50 -X Piston speed mm/s Piston speed mm/s Piston speed mm/s Piston speed mm/s Technical Data 1547 CY1F Series Precautions at Vertical Operation and Intermediate Stop Vertical Actuation 1.
Weight [kg] 10.6 18.5 1 Conductance is the value for the elbow with the same dimensions. For valve heater specifications, refer to Common Option [1] Heater on page 5.
Load mass kg Load mass kg Load mass kg 4 4 4 4 3 3 3 3 CY1F15 CY1F10 CY1F10 CY1F10 2 2 2 2 CY1F10 1 1 1 1 0.5 500 300 100 50 0.5 500 300 100 50 0.5 500 300 100 50 0.5 500 300 100 50 Piston speed mm/s Piston speed mm/s Piston speed mm/s Piston speed mm/s 8-16-7 7 Series CY1F Vertical Actuation 1.
CXSJ6P-: 0.009 kg,CXSJ10P-: 0.014 kg 2 Series CXSJ Model Selections Caution Theoretical output must be confirmed separately, referring to the table on page 2.
CXSJ6P-: 0.009 kg,CXSJ10P-: 0.014 kg 2 Series CXSJ Model Selections Caution Theoretical output must be confirmed separately, referring to the table on page 2.
per square mtr Newton Earth acceleration m I m2 mt m s'' s ' m s-2 m2 kg N a,F,1-6,e.p A,S v v a) J F G = kg ' rn's'2 9.80665 m's-2 N Impulse Ns Newton Second w E , W E , W M P Work Potential energy Kinetic energy Torque Power Joule = Newton meter Joule Joule Joule Watt J J t ' J w = kg . m2's-2 0.5-m-i = J's-l 3.
) Wv: Allowable load weight for vertical operation (kg) Presence of switches P: Operating pressure (MPa) U: Maximum Speed (mm/s) Stroke (mm) Mode of operation (horizontal, inclined, vertical) W: Load weight (kg) WB: Connection fitting weight (kg) : Guide's coefficient of friction L0: Distance from cylinder shaft center to work piece point of application (cm) L1: Distance from cylinder
per square mtr Newton Earth acceleration m I m2 mt m s'' s ' m s-2 m2 kg N a,F,1-6,e.p A,S v v a) J F G = kg ' rn's'2 9.80665 m's-2 N Impulse Ns Newton Second w E , W E , W M P Work Potential energy Kinetic energy Torque Power Joule = Newton meter Joule Joule Joule Watt J J t ' J w = kg . m2's-2 0.5-m-i = J's-l 3.
300 (kg) 0.84 0.97 1.14 1.43 1.58 1.64 1.85 2.09 2.52 2.78 3.10 3.34 [kg] 0.12 0.19 1 2 3000[mm/s 2] 320%(F.S.) 450%~95% 7.2[]P41 LEY 5 6() 452000Hz 1 () 7 8 9 10 11 -14- 3.2.
MB Series Air Cylinder RoHS 32, 40, 50, 63, 80, 100, 125 MB Series 10% lighter CJ1 (40-100 stroke) CJP Weight CJ2 JCM CM2 Current model CM3 1.01 kg 0.91 kg CG1 CG3 JMB Reduced weight by changing the shape of the rod cover and head cover.
Lock unit Cylinder Holding force improved by 15% (MNB, 50: 1370 N a MWB: 1570 N) High stopping accuracy within 1 mm (With 50 and 30 kg of load) Overall length reduced by 18 mm max.
Weight accessories [kg] 32 40 50 63 80 100 L 0.16 0.20 0.38 0.46 0.89 1.09 F 0.20 0.23 0.47 0.58 1.30 1.81 C 0.16 0.23 0.37 0.60 1.07 1.73 D 0.20 0.32 0.45 0.71 1.28 2.11 Example: : Cylinder 40 mm, Stroke 100 mm, bracket D Weight = 0.84 kg + (0.16 kg x 100 ) + 0.32 kg = 1.48 kg 50 Construction Principles Steel balls Spring lock (exhaust lock) The spring force which acts upon the taper ring
164.0 HC-KFS43B 156.5 2.1 SGMAH-04AAA2B 164.0 2.2 HC-MF43B 156.5 2.1 HC-KQ43B 146 2.1 Matsushita Electric Industrial Co., LTD Length(mm) Weight(kg) MSM042P1A 124 1.6 MSMA04A1A 124 1.6 MSM042P1B 157 2.0 MSMA04A1B 157 2.0 Mitsubisi Electric Corporation Length(mm) Weight(kg) Yaskawa Electric Corporation Length(mm) Weight(kg) OMRON Corporation Length(mm) Weight(kg) 3.4 3.4 HC-MFS73 142 3.0 SGME
Eccentricity 200 mm 1 10 10 0.1 Weight m (kg) Weight m (kg) Weight m (kg) 1 1 20 16 20 16 10 6 20 16 10 6 0.01 0.1 0.1 10 6 0.01 0.001 0.01 80 100 0 20 40 60 80 100 0 20 40 60 80 100 0 20 40 60 Overhang L (mm) Overhang L (mm) Overhang L (mm) Selection Example 1.
Heat generation amount by users equipment Q : Unknown [W] ([J/s]) Circulating fluid : Tap water* Example of current measurement units (Reference) Circulating fluid mass flow rate qm : (= x qv 60) [kg/s] Circulating fluid density : 1 [kg/L] Circulating fluid (volume) flow rate qv : 35 [L/min] Circulating fluid specific heat C : 4.186 x 103 [J/(kgK)] Circulating fluid outlet temperature
D0.01 20 40 60 80 100 0 -X Overhang L (mm) 17 MXH Series Selection Graph v to 2 (Horizontal Mounting) Maximum Speed 100 mm/s or Less Maximum Speed 500 mm/s or Less Maximum Speed 300 mm/s or Less Graph 0 Load Eccentricity 50 mm Graph m Load Eccentricity 50 mm Graph v v Load Eccentricity 50 mm 1 100 10 Mass m (kg) Mass m (kg) Mass m (kg) Mass m (kg) 1 10 20 16 20 16 10 6 0.1 20 16 10 6 1 0.1
Rod end configuration: Roller Example 1 Example 2 Transfer speed: 15 m/min Weight of transferred object: 60 kg Friction coefficient = 0.1 Rod end configuration: Lever Weight of transferred object m [kg] Friction coefficient
/Japanese 1 pc.), Y-strainer 20A 1 pc., Barrel nipple 20A 1 pc., Drain pan for the pump Weight (dry state) 377 lbs (171 kg) 390 lbs (177 kg) Note 5) q Ambient temperature: 90F (32C), w Circulating fluid: Tap water, e Circulating fluid temperature: 68F (20C), r Load: Same as the cooling capacity, t Circulating fluid flow rate: Rated flow, y Power supply: 200 VAC, u Piping length: Shortest
In terms of specific load conditions, this allowable kinetic energy is equivalent to a load of 3.7 kg in weight, and a piston speed of 300 mm/sec. Therefore, if the operating conditions are below these values, there is no need to calculate. 2. Apply the following formula to obtain the kinetic energy of the load. Ek: Kinetic energy of load (J) m: Load weight (kg) : Piston speed (m/s) 3.
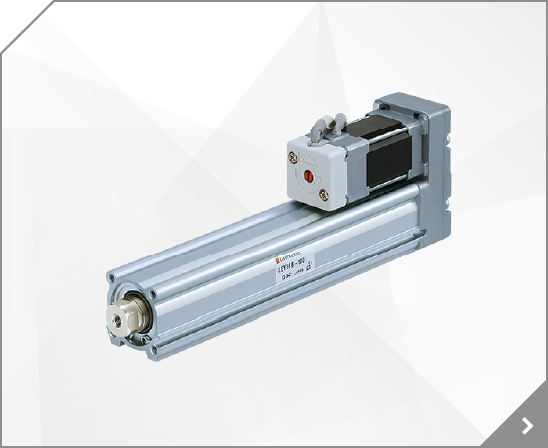
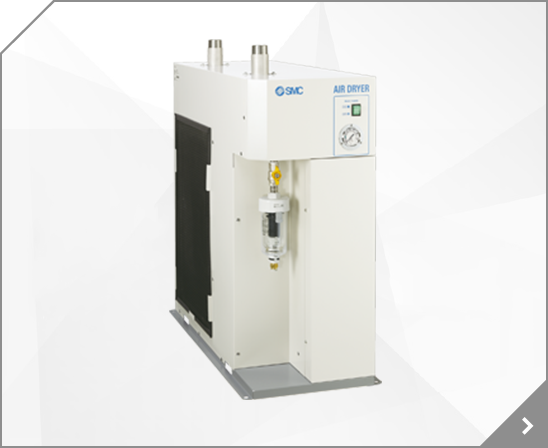
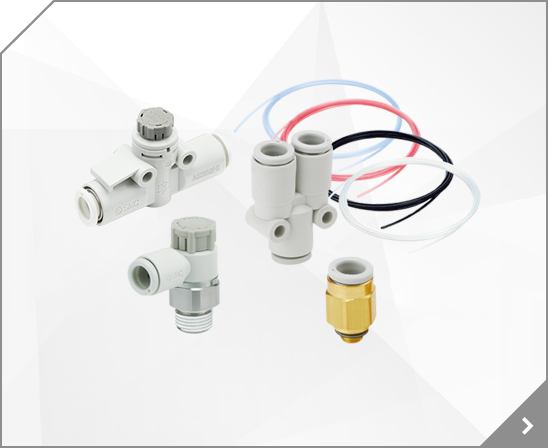
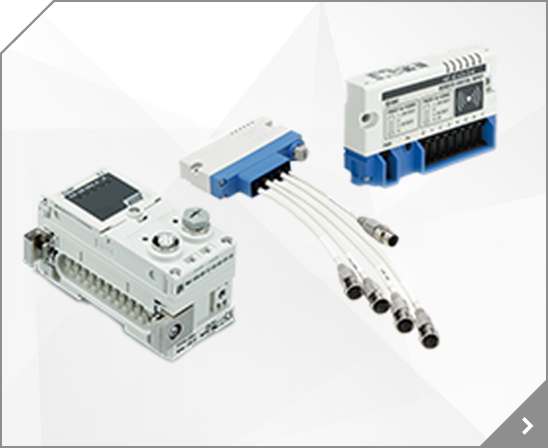










 Low Profile Guide Type
Low Profile Guide Type