
Size: 37.5 O.D., Display Pressure: 0.2MPa, 30psi, Connection Thread: NPT 1/8, Clear Cover Material: Polycarbonate, Attachment: w/o Cover Ring Assembly/None, Option: Both MPa and psi
pump P2 P2 Piping It is recommended to mount a silencer in the EXH port and the bleed port for noise reduction and dust entry prevention.
3 IN(P1) r OUT(P2) VXB B A OUT(P2) A B VXE IN(P1) C C IN(P1) e e q w VXP q w VXD2A VXD2B VXR !4 i VXH !4 u u !0 VXF A B !1 i VX3 !2 !0 !2 VXA o !1 t !3 o OUT (P2) w IN(P1) !3 B r OUT(P2) A r IN (P1) e C e IN(P1) C q w q VXD2E, 2F, 2G VXD2C, 2D Component Parts Operation
The valve element for the C.O. type, which has no return spring, is in an arbitrary position when air is exhausted through the ports P1 and P2. When pressurized air enters the port P1 (exhaust from the port P2), the valve element opens, and it closes when pressurized air enters the port P2 (exhaust from the port P1).
The value of the effective area S, like that of sonic conductance C, expresses the ease of flow. (3) Formula for flow rate When P2 + 0.1 0.5, choked flow P1 + 0.1 293 Q = 120 x S (P1 + 0.1) (3) 273 + T When P2 + 0.1 > 0.5, subsonic flow P1 + 0.1 293 Q = 240 x S (P2 + 0.1) (P1 P2) (4) 273 + T Conversion with sonic conductance C: S = 5.0 x C(5) Q : Air flow rate [L/min (ANR)] S : Effective
The value of the effective area S, like that of sonic conductance C, expresses the ease of flow. (3) Formula for flow rate When P2 + 0.1 0.5, choked flow P1 + 0.1 293 Q = 120 x S (P1 + 0.1) (3) 273 + t When P2 + 0.1 > 0.5, subsonic flow P1 + 0.1 293 Q = 240 x S (P2 + 0.1) (P1 P2) (4) 273 + t Conversion with sonic conductance C: S = 5.0 x C(5) Q : Air flow rate [dm3/min (ANR)], dm3
This is the same concept representing the easy to run through as sonic conductance C. (3) Formula for flow rate P1 + 0.1 P2 + 0.1 When 0.5, choked flow 293 Q = 120 x S (P1 + 0.1) .(3) 273 + t P1 + 0.1 P2 + 0.1 When > 0.5, subsonic flow 293 Q = 240 x S (P2 + 0.1) (P1 P2) .(4) 273 + t Conversion with sonic conductance C: S = 5.0 x C .(5) Q : Air flow rate [dm3/min(ANR)], dm3 (cubic decimeter
VXS VXS VXB VXE (3) Formula for flow rate When P2 + 0.1 0.5, choked flow P1 + 0.1 293 Q = 120 x S (P1 + 0.1) (3) 273 + T When P2 + 0.1 > 0.5, subsonic flow P1 + 0.1 293 Q = 240 x S (P2 + 0.1) (P1 P2) (4) 273 + T Conversion with sonic conductance C: VXP VXR VXH VXF VX3 VXA S = 5.0 x C(5) Q : Air flow rate[L/min(ANR)] S : Effective area [mm2] P1 : Upstream pressure [MPa] P2 : Downstream
This is the same concept representing the easy to run through as sonic conductance C (effective area). (3) Formula of flow rate When P2 + 0.1 0.5, choked flow P1 + 0.1 293 Q = 120 x S (P1 + 0.1) (3) 273 + t When P2 + 0.1 > 0.5, subsonic flow P1 + 0.1 293 Q = 240 x S (P2 + 0.1) (P1 P2) (4) 273 + t Conversion with sonic conductance C: S = 5.0 x C(5) Q :Air flow rate[dm3/min(ANR)], dm3 (
When P2 + 0.1 b, choked flow P1 + 0.1 293 Q = 600 x C (P1 + 0.1) (1) 273 + t When P2 + 0.1 > b, subsonic flow P1 + 0.1 2 P2 + 0.1 b P1 + 0.1 Q = 600 x C (P1 + 0.1) 1 (2) 1 b 293 273 + t Q : Air flow rate [dm3/min (ANR)], dm3 (Cubic decimeter) of SI unit are also allowed to described by l (liter). 1 dm3 = 1 l .
In contrast with the N.C., when air is exhausted from the port 10(P2), the return spring opens the valve element. Pressurized air that enters through the port 10(P2) closes the valve element. Component Parts Material Bronze No.
Example: The figure below is based on the condition of set values as P1 = 40 [kPa] and P2 = 20 [kPa].
The valve element of the C.O. type, which has no return spring, is in an arbitrary position when air is exhausted through the ports 12(P1) and 10(P2). When pressurized air enters the port 12(P1) (exhaust from the port 10(P2)), the valve element opens, and it closes when pressurized air enters the port 10(P2) (exhaust from the port 12(P1)). Component Parts No.
(Return spring normally open) In contrast with the N.C., when the pilot solenoid valve is not energized (or when air is exhausted from the port 10(P2) of the air operated type), the valve body is opened by the return spring. When the pilot solenoid valve is energized (or when pressurized air enters through the port 10(P2) of the air operated type), the valve body closes.
Pilot port P1 and P2 piping Please arrange P1 and P2 piping as follows according to the model.
Circuit example (1) Circuit example (2) 3 port solenoid valve 4 port solenoid valve 5 port solenoid valve (Exhaust center) Throttle Regulator Mist separator Micro mist separator Process Pump Throttle Mist separator Micro mist separator FLUID OUT Process Pump Air supply Regulator P1 FLUID OUT P1 P2 Air supply Strainer P2 FLUID IN Strainer FLUID IN Transfer fluid Transfer fluid For the related
Setting Spring Diaphragm p2 PI alve Spring When consumption starts, pA will initially drop and the spring, momentarily stronger than the lifting lorce {rom p2 on th diaphragm, opens the valve. Fig 5.5.
The valve element of the C.O. type, which has no return spring, is in an arbitrary position when air is exhausted through the 12(P1) and 10(P2) ports. When pressurized air enters the 12(P1) port (exhaust from the 10(P2) port), the valve element opens, and it closes when pressurized air enters the 10(P2) port. LVH LVD LVQ LQ LVN Component Parts No.
Setting Spring Diaphragm p2 PI alve Spring When consumption starts, pA will initially drop and the spring, momentarily stronger than the lifting lorce {rom p2 on th diaphragm, opens the valve. Fig 5.5.
In contrast with the N.C., when air is exhausted from the P2 port, the return spring opens the valve element. Pressurized air that enters through the P2 port closes the valve element. 0 4 Component Parts No.
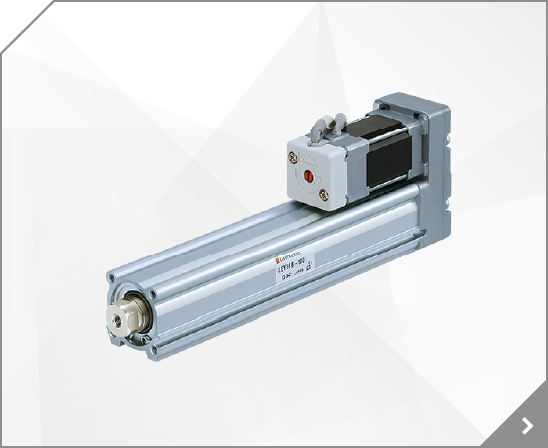
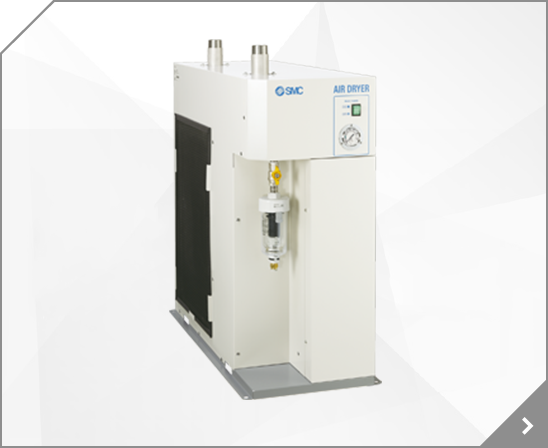
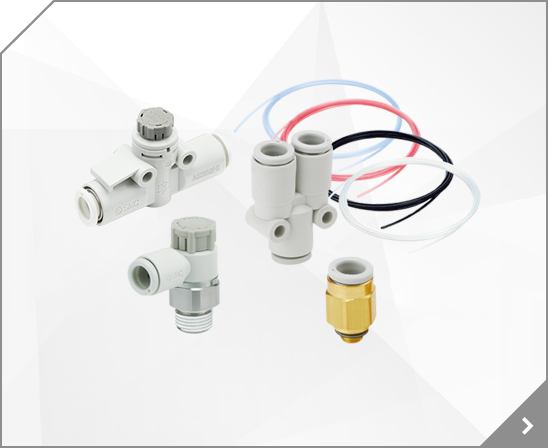
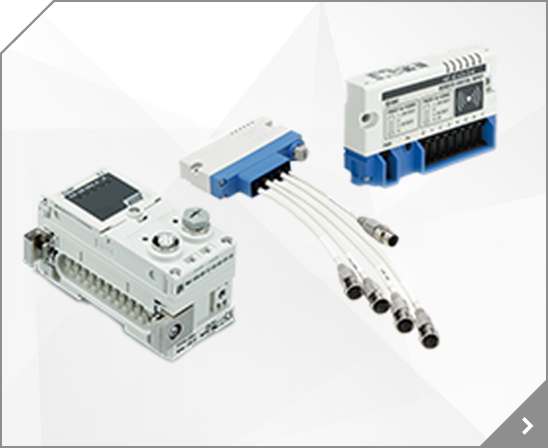
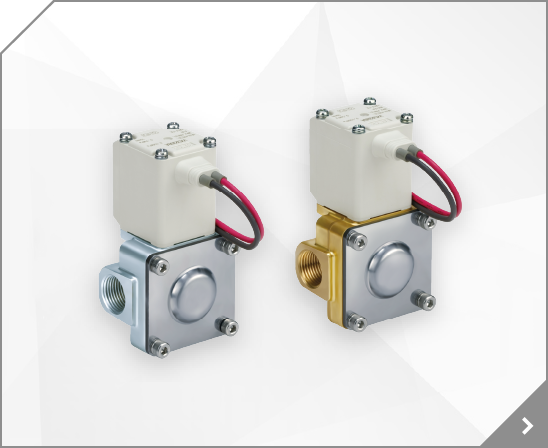










 2/3 Port Valve
2/3 Port Valve