
MK/MK2 RSQ/RSG RSH CE1 CE2 ML2B ML1C REA Calculation for Moment of Inertia I: Moment of Inertia (kgm2) m: Load weight (kg) REC qThin bar Position of rotary axis: Vertical to the bar and through the end rThin rectangular plate Position of rotary axis: Vertical to the plate and through the end RHC a22 3 I = m1 + m2 4a12+b2 12 4a22+b2 12 I = m1 + m2 a12 3 MTS CC wThin bar Position of rotary
Position of rotation axis: Parallel to side b and passes a center of gravity. 1=m 12 a 2 1=m 4 r 2 oWith a load at the lever end rThin rectangle board (Parallelogram) Position of rotation axis: Perpendicular to the board and passes through center line. 2 1 2 2 a +K 1=m1 +m2 3 a Ex.)
L1 L2 T M5 type H (width across flats) Applicable tubing O.D. d A A4 D1 L3 D2 M1 L1 T L2 Model Weight (g) Note 2) Tubing O.D. d T H D1 D2 L1 L2 L3 M1 L4 Max.
Cylinder (including thin round plate) Position of rotational axis: Through the plate's central axis Position of rotational axis: Perpendicular to the shaft anywhere along its length I = m1 x + m2 x 3 a1 3 a2 I = m x 2 r 2. Thin shaft Position of rotational axis: Through the shaft's center of gravity 7.
L1 L2 T M5 type H (width across flats) Applicable tubing O.D. d A A4 D1 L3 D2 M1 L1 T L2 Model Weight (g) Note 2) Tubing O.D. d T H D1 D2 L1 L2 L3 M1 L4 Max.
D1 Port B min. port size Weight (g) D2 L1 L2 L3 L4 P Q1 Q2 M1 M2 4 4 6 KM16-06-06-3 12.8 4 6 KM16-04-04-3 16 17 17 KM16-04-06-3 6 16 16 17 19 18 3 4.5 18 4.5 12.8 68 20.9 16 11 14.5 50 10.5 65
W: Work load (N) L1, L2, L3: Amount of overhang to work piece center of gravity (mm) a: Table acceleration (mm/s) Mounting position Direction of load movement Model LJ1H10 LJ1H20 LJ1H30 Horizontal/Lateral Horizontal/Lateral Vertical Lateral Horizontal a M1 2000 a=1000 a=1000 2000 2000 a=1000 L1 mm L1 mm L1 mm Pitching W a=2000 a=2000 a=3000 a=3000 a=2000 1000 1000 1000 L1 a=3000 0 2 4 6 8
M1 L M2 D 4 KCH04-00 KCH06-00 KCH08-00 KCH10-00 KCH12-00 42.1 45.8 52.8 59.8 63.5 10.4 12.8 15.2 18.5 20.9 2.6 6.8 16.2 25.6 35.4 18 19 21.5 24 25.5 16 17 18.5 21 22 2.6 6.8 13.1 20.4 30.4 5 8 11 18 24 6 8 10 12 Note) D: max. diameter Straight plug for frequent use: KCH Applicable tube O.D.
0Gear transmission oLoad at lever end Number of teeth = a = m1 a12 1. Find the inertial moment B for the rotation of shaft (B). 3 + m2 a22 + K (Example) When shape of m2 is a sphere, refer to 7, and K = m2 2r2 2.
This is a legacy product. Please contact us for the latest version.sales@ocaire.com, VACUUM EJECTOR, COMPACT, VACUUM SERIES, ZA COMPACT VACUUM EJECTOR, BG, ZA NOZZLE SIZE 0.5, .43375 lb
As a guide, when W + P0a > P0A, adjust P1, so that it could be W + P1a = P0A. (1) The speed is controlled with meter-out control. When the meterin controller is used in conjunction with the meter-out controller, lurching is reduced. () (2) Installing a regulator with check valve at position (b) can decrease lurching during descent, and actuation delay during ascent.
fitting dimension Y W Plate thickness ARP20(K), ARP30(K) : Max. 3.5 ARP40(K) : Max. 5 OUT IN 1021 1021 Z Pressure Gauge Option Digital pressure switch (Electrical entry: Wiring top entry) Digital pressure switch (Electrical entry: Wiring bottom entry) Option Round type pressure gauge J J J H Dimensions Center of piping H Center of piping H Center of piping Standard specifications Model P1
Example) Lead wire length 2000 mm Electrical entry When ordering cylinder with valve CVQM32-30-M9B-5MOZ SY100-30-4A-20 M-type plug connector with lead wire (Lead wire length 300 mm) M MO M-type plug connector without connector 5 Series CVQM Dimensions 32 to 63 EXH 2 x P2 F SUP P1 S S Q 2 x HB through Manual button 2 x HA through V W 2 x 2 x OA effective length RA KA 2 x N through Y EB (KB
Flow rate characteristics: C Max. operating frequency 0.8 MPa 0.15 MPa 5 to 50C 0.60 dm3/(sbar) 180 c.p.m SZ SUP side pressure (P1) To CYL port VVQ1000-FPG-02 1 set VQ1000-FPG-C6M5-D 2 pcs.
P1 70W XGT Kalrez Q1 R1 R2 R3 S1 T1 4079 SS592 SS630 SSE38 1232-70 3310-75 To order something else Nil (standard), list the symbols starting with X, followed by each symbol for "body surface treatment", "seal material" and then changed parts at last. CYV Chemraz Example) XLAQ-25-M9NA-XAN1A VMQ FKM for Plasma ULTIC ARMOR U1 UA4640 Produced by Mitsubishi Cable Industries, Ltd.
Pmax Vacuum pressure P1 1. If the ejectors suction port is closed and sealed tight, the suction flow becomes 0, and the vacuum pressure increases to the max. (Pmax). 2. If the suction port is opened gradually and air is allowed to flow (the air leaks), the suction flow increases, and the vacuum pressure decreases. (The condition of P1 and Q1) 3.
At this time, read vacuum pressure P1, obtain the suction flow rate from the flow-rate characteristics graph for the ejector that is being used, and render this amount as the leakage of the workpiece.
At this time, read vacuum pressure P1, obtain the suction flow rate from the flow-rate characteristics graph for the ejector that is being used, and render this amount as the leakage of the workpiece.
Set pressure Inlet pressure P1: 0.5 MPa Outlet pressure P2: 0.1 MPa Fluid: Water Model: SRF30 0.5 Inlet pressure 0.45 Piping Caution 0.4 Pressure (MPa) 0.35 0.3 1. Connecting tubes with special tools. Refer to the pamphlet: High-Purity Fluoropolymer Fittings Hyper Fittings/LQ1,2 Series Work Procedure Instructions (M-E05-1) for tube connection and special tools. 2.
Flow Characteristics Air pressure 0.7 MPa (Example) To get pressure drop at 0.3 MPa of air pressure, 2000 l/min (ANR) of air flow, and model HAA22, use P = 0.0007 MPa from the table and convert P1 to 0.3 MPa.
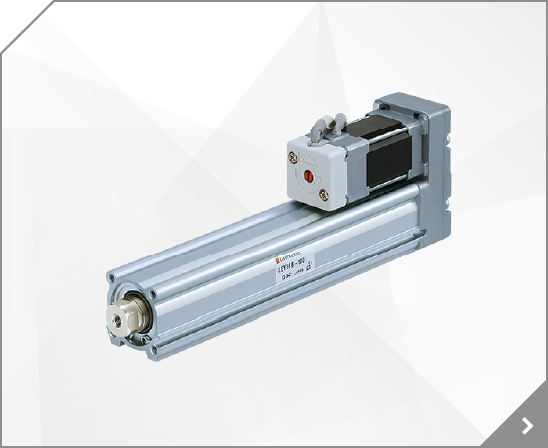










 MK
MK