
XLGV/With solenoid valve Q Port R (exhaust port) N N With double solenoid P K M L (mm) L 6.5 6.5 6.5 11 11 11 K 9 9 9 11 11 11 N 14 Model K L M N P Q M 17 15 2 6 Q 16.5 16.5 17.5 28 29 29 P Model XLGV-16 XLGV-25 XLGV-40 XLGV-50 XLGV-63 XLGV-80 3 3 3 6.5 6.5 6.5 16 With single solenoid Port P (pressure port) 29 26 32 45 Other dimensions are the same as XLG. 19 Series XLD, XLDV Smooth Exhaust
VZ (A) 2 (A) 2 VS 3 (R) 1 (P) 3 (R) 1 (P) r e w q r e w q N.O. N.O. (A) 2 (A) 2 3 (R) 1 (P) 3 (R) 1 (P) Component Parts Material Description Notes No.
XLGV/With solenoid valve Q Port R (exhaust port) N N With double solenoid P K M L (mm) L 6.5 6.5 6.5 11 11 11 K 9 9 9 11 11 11 N 14 Model K L M N P Q M 17 15 2 6 Q 16.5 16.5 17.5 28 29 29 P Model XLGV-16 XLGV-25 XLGV-40 XLGV-50 XLGV-63 XLGV-80 3 3 3 6.5 6.5 6.5 16 With single solenoid Port P (pressure port) 29 26 32 45 Other dimensions are the same as XLG. 19 Series XLD, XLDV Smooth Exhaust
Standard type (through hole, double end tapped common)/RQB, RDQB 2-M5 x 0.8 (port size) 2-cushion needle 2 x 4-9 depth of counter bore 7 H thread effective depth C E1 E2 Q F 4-5.4 through D M E 1 Flat washer 4 pcs.
Moment (Nm) Payload (N) ML1C/M2,M3 How to calculate the load ratio A. Consider q Max. payload, w static moment, e dynamic moment (when stopper collides) when calculating the Max. allowable moment and payload. Evaluate q and w as a (average speed), and e as (collision speed =1.4a).
-20D MHS2-25D G 25 27 28 FZ 3 3 5 FY 11 13 14.5 FX 12.5 14.5 17 CB 11 13 15 EC 10 12 14 EO 14 16 20 NB 5h9 6h9 6h9 DC 30 36 42 NA 8 10 12 DO 34 40 48 K 4 5 6 B 30 36 42 Q 6 7 8 J 10 12 14 AA 35 38 40 AB 32 35 37 O 2 2.5 3 P M3 x 0.5 M5 x 0.8 M5 x 0.8 0 -0.030 0 -0.030 0 -0.030 Model MHS2-16D MHS2-20D MHS2-25D VA 2H9 2H9 3H9 TB 5 6 6 SC 8 9.5 10 RB 16 18 22 RA 18 24 26 WA VB 2 2 3 XA 2H9 2H9
Air Flow Max. flow line Pressure drop (MPa) Max. air flow rate (m3/min (ANR)) Air flow rate (l /min (ANR)) Model Selection Select the model in accordance with the following procedure taking the inlet pressure and max. air flow into consideration. (Example) Inlet pressure: 0.6 MPa Max. air flow capacity: 5 m3/min (ANR) 1.
Max. air flow rate (m3/min (ANR)) JIS Symbol P . 14-20-55 Inlet pressure (MPa) Caution Be sure to read before handling.
3 u q !9 y @7 @0 @6 @5 @4 Auto switch !8 @1 @2 !6 !1 @3 !7 !0 !5 !
0 e New PFA q Body New PFA w Sensor Super PFA e Tube PPS r Housing A PPS t Housing B PPS y Housing C POM u Bushing PPS i Cap FKM o Gasket FKM !0 O-ring Stainless steel 304 !1 Thread PVC !2 Lead wire !1 q t i PF2D540 o !0 u !0 !2ywr e !
The smoothness of the surface and closeness of the oxidize layer can effect (increase/decrease) this. 7 Ultimate pressure Ultimate pressure is P=Q/S, where the sum of mass flow rates for outgassing (Qg) and leakage (Ql) is Q(Pam3/s), and the exhaust speed is S(m3/s). The ultimate pressure is measured with Qg, QlS shown as above, and the ultimate pressure of the pump itself.
VP300-224-1 (M3 x 36) VP500-224-1 (M4 x 46) VP700-224-1 (M5 x 66) Thread type Series For valve mounting 3 5 7 VPA344 VPA544 VPA744 Nil F N T Rc G NPT NPTF Caution Tightening Torque of Mounting Screw Port size Symbol 1 2 VPA344 1/8 1/4 VPA544 1/4 3/8 VPA744 3/8 1/2 M3: 0.8 Nm M4: 1.4 Nm M5: 2.9 Nm 1565 VPA300/500/700 Series VPA300 Series/Base Mounted/Dimensions Standard/VPA344-101 02 A B
0 u #0 $2 #6 t #8 q y $0 $1 20 r !1 e @2 #7 #3 #1 !2 32 w 50, 63, 80 @3 Double acting (DL, DM) !3 !5 #6 o @5 i @1 @4 @6 !0 @7 @9 !6 t i !7 q !8 #8 $1 Single acting (TL, TM) Double acting built-in spring (BL, BM) $0 y r !1 #7 e #4 #7 !
Pressure dew point: 3C Oil concentration: 0.1 mg/m3 With the above conditions, notation of the quality class is 1, 4, 2. 344 LLB Series Clean Air Module / Precautions 2 Be sure to read this before handling the products.
5st 10st Z Bore (mm) 6 10 15 A 15st 7 12 13.9 6 12.5 19.5 26.5 8.5 9 3.5 M3 X 0.5 M10 X 1.0 9 18.5 25.5 32.5 3 27.5 34.5 41.5 3 10 19 22 6 14.5 21 28 12 12 3.5 M4 X 0.7 M15 X 1.5 13 20.5 27 34 4 32.5 39 46 5 12 27 31 7 16.5 22.5 29 19 14 4.2 M5 X 0.8 M22 X 1.5 20 23.5 29.5 36 5 37.5 43.5 50 6 Plug Mounting Style CJPS B C E G H K MM NN 5st 10st F 15st R 5st 10st S 15st W Q 5st 10st Z Bore
(Not a\ailabl on NCRBI BWl0) x ( ) : When porl A is pressunzed. x x Optional M3 fiiing available S ho/r lo ofder page NCDRBIOWIQoI$ol[r$Q Rotation Time Setting Bodg To k Used As A Flange ltcRElB\ltfto Actual Torque Even a small torque generated by the rotary actuator, due to inertia, can cause damage. Therefore.
STATION X1 5 5 6 6 4 4 7 7 3 3 2 2 8 8 5 1 1 9 9 0 0 0 5 5 1 1(1) 0 0 0 10(0) 3.2.4 CC-Link(MODE) 156kbps CC-Link 0() 156kbps MODE 1 625kbps 5 4 6 2 2.5Mbps 3 7 3 5Mbps 5 2 8 0 4 10Mbps 9 1 0 5 5 59 0 0 3.2.5 (SW1) 3.2.3 1 SW1 1 ( ) 5 0 5 5 2 0 0 3 8 3CC-Link 3.3 3.3.1 CC-Link (1) CC-Link3.518ms(512) CC-Link (2) I/O C P U (3) FROMCC-Link TOFROM/TO, CC-Link CC-Link C C C C Q
How to Find the Flow Rate (at air temperature of 20C) Subsonic flow when P1 + 0.1013 < 1.89 (P2 + 0.1013) Q = 226S P(P2 + 0.1013) Sonic flow when P1 + 0.1013 1.89 (P2 + 0.1013) Q = 113S (P1 + 0.1013) Q: Air flow rate [l/min (ANR)] S: Effective area (mm) P: Differential pressure (P1P2) [MPa] P1: Upstream pressure [MPa] P2: Downstream pressure [MPa] Correction for different air temperatures
(Not a\ailabl on NCRBI BWl0) x ( ) : When porl A is pressunzed. x x Optional M3 fiiing available S ho/r lo ofder page NCDRBIOWIQoI$ol[r$Q Rotation Time Setting Bodg To k Used As A Flange ltcRElB\ltfto Actual Torque Even a small torque generated by the rotary actuator, due to inertia, can cause damage. Therefore.
Calculate (1) (Wmax) from the graph of max. payload (W1, W2, W3) and calculate (2) and (3) (Mmax) from the maximum allowable moment graph (M1, M2, M3).
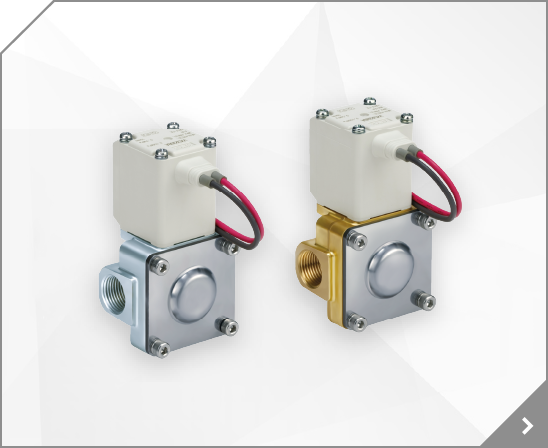










 High Vacuum Angle Valve, XL Series
High Vacuum Angle Valve, XL Series