
When P2 + 0.1 b, choked flow P1 + 0.1 293 Q = 600 x C (P1 + 0.1) (1) 273 + t When P2 + 0.1 > b, subsonic flow P1 + 0.1 2 P2 + 0.1 b P1 + 0.1 Q = 600 x C (P1 + 0.1) 1 (2) 1 b 293 273 + t Q : Air flow rate [dm3/min (ANR)], dm3 (Cubic decimeter) of SI unit are also allowed to described by l (liter). 1 dm3 = 1 l .
When P2 + 0.1 b, choked flow P1 + 0.1 293 Q = 600 x C (P1 + 0.1) (1) 273 + t When P2 + 0.1 > b, subsonic flow P1 + 0.1 2 P2 + 0.1 b P1 + 0.1 Q = 600 x C (P1 + 0.1) 1 (2) 1 b 293 273 + t Q : Air flow rate [dm3/min (ANR)], dm3 (Cubic decimeter) of SI unit are also allowed to described by l (liter). 1 dm3 = 1 l .
* O . b 3 z o 1 0 0 6 o u o q ; N q * E 9 . " o . 5 " > 2 4 ' ;l l.:, . . o o o 2 4 6 8 1 0 1 2 1 4 1 6 1 8 2 0 TOTAL ENERGY ( nrbtc) (Tho!ends) Note: Minimum impact velocity tor PM nlodels it 4 itr/*c. 9k**k &"bs*rbers Non-Adjustable Hydraulic Series 49rc.
D-K39 D-A5 D-A6 D-A59W D-F5NTL D-P5DWL Bore size (mm) A A B A B A A A A B B B B B 32 12 7 4.5 0 0.5 3.5 4 0.5 9.5 4.5 2 1 1.5 0 CJ1 40 12 7 4.5 0 0.5 3.5 4 0.5 9.5 4.5 2 1 1.5 0 50 12.5 7.5 5 0 1 4 4.5 1 10 5 2.5 1.5 2 0 CJP 63 12.5 7.5 5 0 1 4 4.5 1 10 5 2.5 1.5 2 0 80 15.5 10.5 8 2.5 4 7 7.5 4 14 9 6.5 5.5 6 2.5 CJ2 100 15.5 10.5 8 2.5 4 7 7.5 4 14 9 6.5 5.5 6 2.5 125 17.5 12.5 10 6 6
KQ2C Caps P Plugs Q Cartridge KR Fitting Boot . . . . . . . .6 .7 .7 .7 P .8 .8 .9 .9 o 't0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 Spucial [nnlhunilions Page 14 IIU lrlylon lltliltg Page 15 Bmss Phe tittittg$ pase N i p p l e s . . . . . . . . . 1 7 Cdinlinars -. -14 Bushings Aalaolers 1 8 '18 1 q Ts6s .20 .20 Pftr^q 21 SAE 45" Flares . -..22-23 .24 General Assembly..,.. lmoortant Oo's and Dont's Chemical
AREA A position 2 The AREA signal is output commonly for the ranges set for both the AREA A and AREA B. AREA B Set as AREA 1 AREA 2. position 1 AREA B position 2 48 - Data (Saved data) Data is sent as hexadecimal numbers.
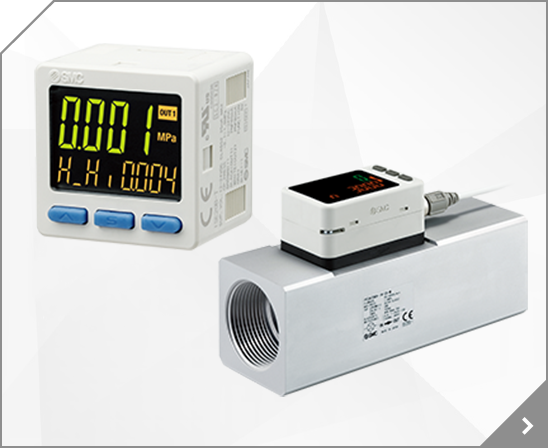
Temperature Data A or B = Series IDUS: Data A Series IDFS: Data B Air pressure Data C = 2 Calculate corrected air flow by using A or B and C. Corrected air flow = (Air flow) (Data A x Data C) Corrected air flow = (Air flow) (Data B x Data C) 3 Select a model having an air flow capacity that is higher than the corrected air flow.
Model Selection 1 Obtain the correction factor for the temperature from data A or B and the correction factor for the air pressure from data C. Temperature Data A or B = Series IDUS: Data A Series IDFS: Data B Air pressure Data C = 3 2 Calculate corrected air flow by using A or B and C.
Temperature Data A or B = Series IDUS: Data A Series IDFS: Data B Air pressure Data C = 2 Calculate corrected air flow by using A or B and C. Corrected air flow = (Air flow) (Data A x Data C) Corrected air flow = (Air flow) (Data B x Data C) 3 Select a model having an air flow capacity that is higher than the corrected air flow.
RIr-,rniTIi n"a I /'i\ v ' _ _ + _ (+) Elcrric Surue aboter D-FsBAUD-JsgW Il',A67 D-A64 D-A59W D-FsP, D.F7P, D-F7 PV D-F5PW D-F59, D-F79, O-F7NV t}F5NTL r+r B-6d Oulput @ I o Elack o L D-J51 r @ D-F59W D-F59F D-.J59, D"J79, Drr7gc, D-F7BV r l lf:r_ rlrtlH-r r-rad t l l l o{tsd OUT 1 output b Diagnoslic ouipul OUT D-472.O-472H D-480. D.A8OH fContu*-r box !
RIr-,rniTIi n"a I /'i\ v ' _ _ + _ (+) Elcrric Surue aboter D-FsBAUD-JsgW Il',A67 D-A64 D-A59W D-FsP, D.F7P, D-F7 PV D-F5PW D-F59, D-F79, O-F7NV t}F5NTL r+r B-6d Oulput @ I o Elack o L D-J51 r @ D-F59W D-F59F D-.J59, D"J79, Drr7gc, D-F7BV r l lf:r_ rlrtlH-r r-rad t l l l o{tsd OUT 1 output b Diagnoslic ouipul OUT D-472.O-472H D-480. D.A8OH fContu*-r box !
Features 2 Model Selection 1 Obtain the correction factor for the temperature from data A or B and the correction factor for the air pressure from data C. Temperature Data A or B = Series IDU: Data A IDF1D to 240D: Data B-1 IDF 370B: Data B-2 Air pressure Data C = Series IDU and Series IDF: Data C 2 Calculate corrected air flow by using A or B and C.
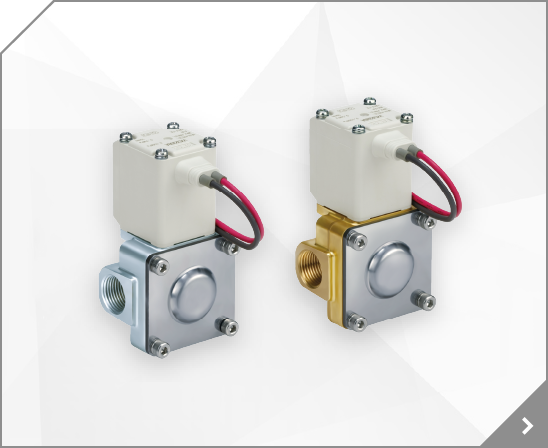
This is a legacy product, and replaced byVNB401B-N25A, PROCESS VALVE *LQA, VALVE, VNA/B/C/D 2-WAY MEDIA VALVE, KA, VNA/B/C/D BODY PT >3/4NPT, 3.08000 lb
This is a legacy product, and replaced byVNB404AS-N25A-B
Compatible Fluid: Coolant, Operating Environment: Standard, Type: Electromagnetic Type, Number of Solenoids: Single Solenoid, Switching Type: Normally Closed, Application: Individual Item, Connection Type: NPT, Plumbing Thread Nominal: 1, Tube Flange Nominal: -, Operating Temperature Range(°C): -5~50, Driving Type: Pilot Type, Orifice Diameter(Ø): 16, Voltage: 24 V DC, Sealing materials:
Size: 4 [ø25(ø16)], Valve Type: 4 [NC (Operating Pressure 1MPa)], Sealant: B (FPM seal), Thread: N (NPT), Port Size: 25A (1), Voltage: 3 (110VAC 50/60HZ), Lead Wire: DZ (DIN Terminal w/Light & Surge Voltage Suppressor), Manual Override: Non-locking Push Style, Bracket: B (Bracket)
Size: 4 [ø25(ø16)], Valve Type: 4 [NC (Operating Pressure 1MPa)], Sealant: B (FPM seal), Thread: N (NPT), Port Size: 25A (1), Voltage: 5 (24VDC), Lead Wire: DZ (DIN Terminal w/Light & Surge Voltage Suppressor), Manual Override: Non-locking Push Style, Bracket: B (Bracket)
Size: 4 [ø25(ø16)], Valve Type: 4 [NC (Operating Pressure 1MPa)], Sealant: FPM seal, Thread: NPT, Port Size: 1, Voltage: 110VAC 50/60HZ, Lead Wire: DIN Terminal w/Light & Surge Voltage Suppressor, Manual Override: Non-locking Push Style, Bracket: Bracket, CE Compliant: -
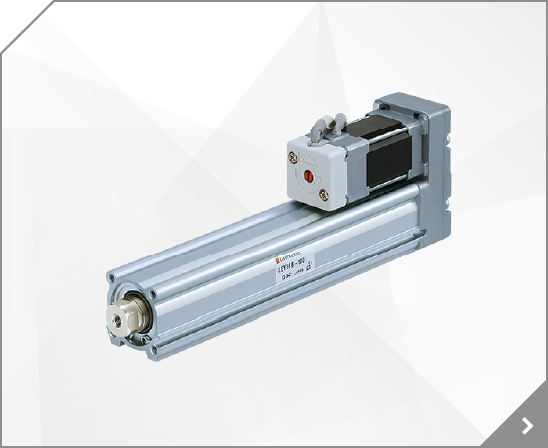
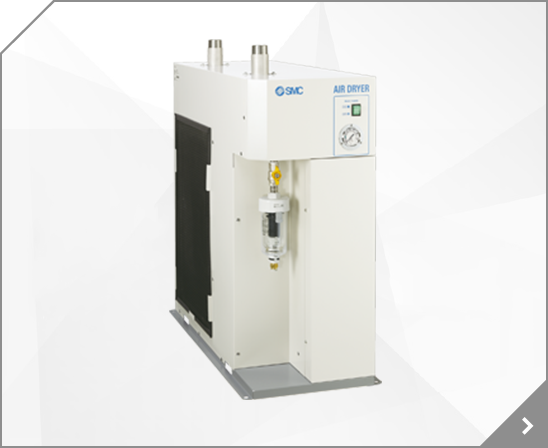
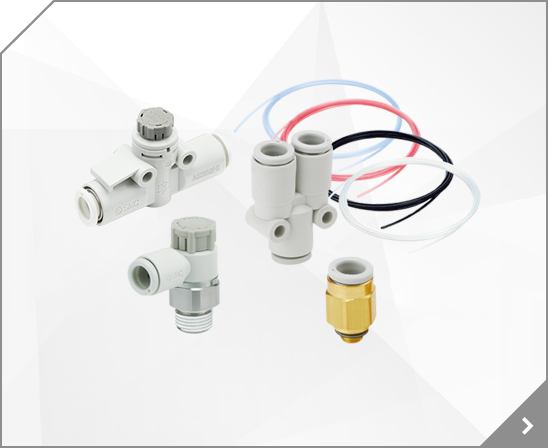
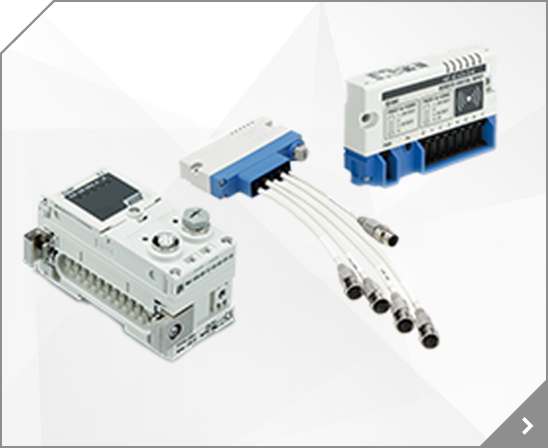










 Model Selection 1
Model Selection 1